TIFF vs JPEG vs PDF (and More): What’s the Difference
When working with digital files, the choice of format can make or break your project. Whether you’re preparing images for print, uploading photos to your website, or sharing important documents, understanding the difference between TIFF, JPEG, PDF, PNG, and GIF is essential. At big Acrlic we work with all of these Formats. Jpeg is the most popular
This guide breaks it down in simple terms ✅
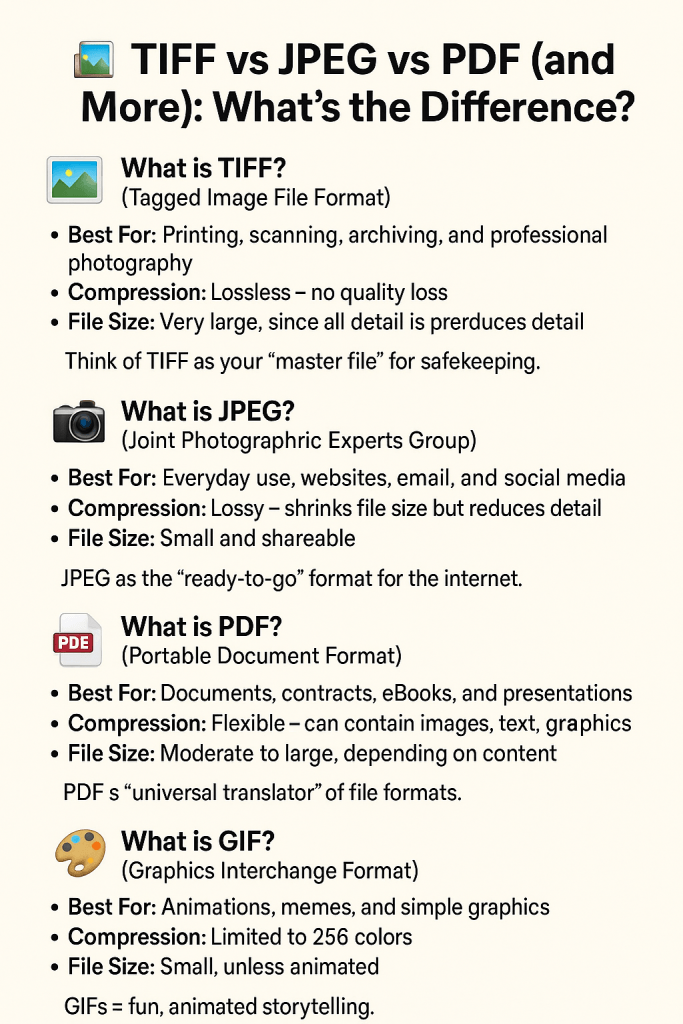
🖼️ What is TIFF? (Tagged Image File Format)
Best For: Printing, scanning, archiving, and professional photography.
Compression: Lossless — no quality loss.
File Size: Very large, since all the detail is preserved.
Use Case: Ideal for graphic designers, printers, and archivists who need every detail intact.
👉 SEO Tip: TIFF is often compared to JPEG because TIFF keeps all the quality, while JPEG compresses it.
✨ Think of TIFF as your “master file” for safekeeping.
📷 What is JPEG? (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
Best For: Everyday use, websites, email, and social media.
Compression: Lossy — shrinks file size but reduces detail.
File Size: Small and shareable.
Use Case: Perfect for web uploads, online portfolios, and quick sharing.
👉 TIFF vs JPEG: JPEG is smaller and faster to share, but TIFF is higher quality for printing.
✨ JPEG is your “ready-to-go” format for the internet.

📄 What is PDF? (Portable Document Format)
Best For: Documents, contracts, eBooks, and presentations.
Compression: Flexible — can contain images, text, and graphics.
File Size: Moderate to large, depending on content.
Use Case: Excellent for sharing documents with guaranteed formatting across devices.
👉 PDF vs JPEG: PDF is for documents with text and images, while JPEG is strictly an image format.
✨ PDF is the “universal translator” of file formats.
🖌️ What is PNG? (Portable Network Graphics)
Best For: Web graphics, logos, and transparent backgrounds.
Compression: Lossless — sharp, clean edges.
File Size: Larger than JPEG, smaller than TIFF.
Use Case: Perfect for logos, icons, and website graphics with transparency.
👉 PNG vs JPEG: Use PNG for crisp logos, JPEG for photos.
✨ PNG = clean and professional visuals online.
🎨 What is GIF? (Graphics Interchange Format)
Best For: Animations, memes, and simple graphics.
Compression: Limited to 256 colors.
File Size: Small, unless animated.
Use Case: Great for short animations, fun graphics, and sharing online humor.
👉 GIF vs PNG: GIF supports motion, PNG does not.
✨ GIFs = fun, animated storytelling.
⚖️ Quick Comparison of File Formats
TIFF 🖼️
Compression: Lossless
Quality: Highest possible
Best Use: Printing, archiving, professional photography
JPEG 📷
Compression: Lossy
Quality: Good, but some detail lost
Best Use: Web, email, social media, casual use
PDF 📄
Compression: Flexible (depends on content)
Quality: Excellent for text and design
Best Use: Contracts, brochures, eBooks, universally viewable docs
PNG 🖌️
Compression: Lossless
Quality: High, sharp edges, supports transparency
Best Use: Logos, icons, clean web graphics
GIF 🎨
Compression: Lossless but limited to 256 colors
Quality: Low for photos, but supports motion
Best Use: Animations, memes, short looping graphics

✅ Final Thoughts
Choose TIFF for professional print jobs and archival storage.
Use JPEG when you need smaller files for web or email.
Go with PDF when formatting and readability matter most.
Pick PNG for sharp, transparent graphics.
Try GIF when you want a touch of fun with animation 🎉
By understanding the differences between TIFF, JPEG, PDF, PNG, and GIF, you’ll always choose the right format for the job.